How Do Flange Bolts Improve Strength in Industrial Applications?
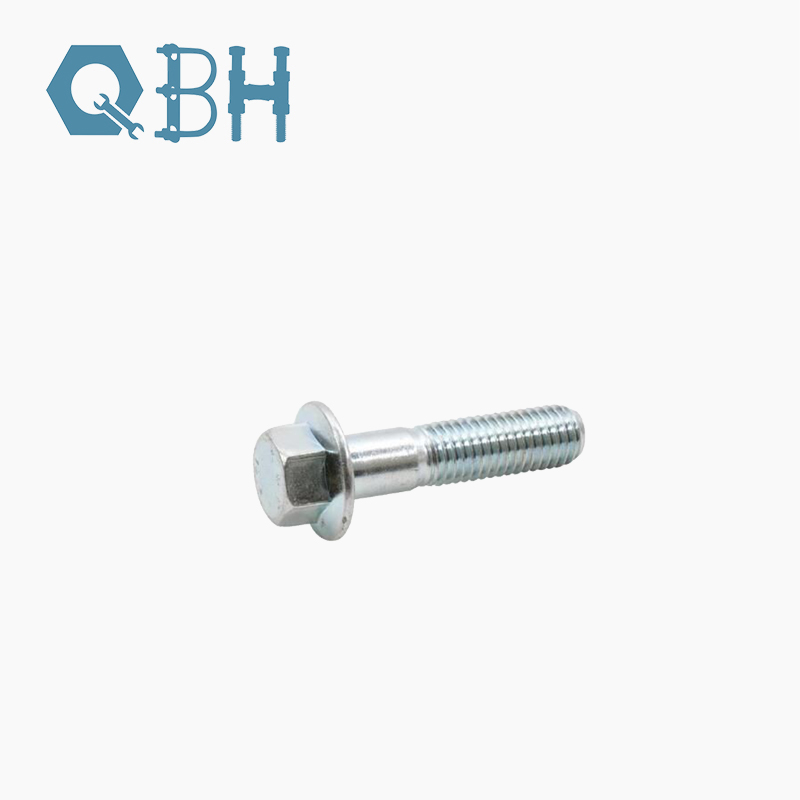
Flange bolts are among the most widely used fasteners in industrial construction, automotive manufacturing, and heavy machinery. Unlike traditional bolts that require a separate washer, flange bolts are designed with an integrated circular flange beneath the head. This flange acts as a built-in washer, distributing load evenly and reducing the risk of damage to the surfaces being fastened.
The engineering behind flange bolts focuses on combining convenience, structural integrity, and long-term durability. By eliminating the need for additional washers, installation becomes faster and more efficient, which is highly beneficial for large-scale operations where thousands of bolts may be used daily.
Flange bolts are commonly found in:
-
Automotive assembly lines (engines, transmissions, chassis connections)
-
Pipeline systems (oil, gas, and water transportation)
-
Heavy-duty machinery (construction equipment, mining machines, agricultural equipment)
-
Steel structure assembly (bridges, towers, industrial plants)
The key working principle of flange bolts is their ability to resist loosening under vibration and heavy loads. The flange design increases surface contact, preventing damage to the connected parts while ensuring long-term fastening reliability.
In terms of standards, flange bolts are manufactured according to international specifications such as ISO, DIN, ANSI, and JIS, ensuring compatibility across industries. Depending on the application, these bolts can be produced in carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel, with different grades of hardness and coatings for corrosion protection.
Why Industries Rely on Flange Bolts: Technical Specifications and Performance Benefits
When evaluating the importance of flange bolts, one must focus on their engineering specifications. Below is a detailed table outlining the common parameters that define flange bolt performance:
| Parameter | Specification Options | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Size Range | M6 – M30 (Metric) / 1/4” – 1 1/4” (Inch) | Covers small to heavy-duty fastening needs across industries. |
| Thread Type | Coarse (UNC), Fine (UNF), Metric | Ensures compatibility with international machinery and components. |
| Head Type | Hex Flange, Serrated Flange | Serrated version provides extra resistance against loosening. |
| Material Options | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel (A2, A4), Alloy Steel | Choice depends on environment and required strength. |
| Strength Grades | 8.8, 10.9, 12.9 (ISO Standard) | Higher grade equals greater tensile strength and durability. |
| Coating / Finish | Zinc Plated, Hot-Dip Galvanized, Black Oxide, Dacromet | Enhances resistance to rust, corrosion, and surface wear. |
| Applications | Automotive, Construction, Machinery, Pipelines | Multi-industry adaptability makes flange bolts highly versatile. |
The benefits of using flange bolts extend beyond convenience:
-
Vibration Resistance – The integrated flange distributes load and reduces loosening caused by machine vibrations.
-
Time Efficiency – No need for additional washers means faster assembly and reduced labor costs.
-
Corrosion Protection – Coatings like zinc plating and hot-dip galvanizing make flange bolts suitable for outdoor and marine environments.
-
High Load Capacity – Grades such as 10.9 and 12.9 provide superior tensile strength, making them suitable for high-pressure applications.
-
Enhanced Safety – The flange reduces the risk of material deformation, keeping structural integrity intact.
By combining these features, flange bolts provide industries with a solution that balances strength, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
How Flange Bolts Compare to Other Fasteners: Practical Applications and Advantages
To understand why flange bolts dominate many industrial fields, it’s helpful to compare them with other fasteners such as standard hex bolts, carriage bolts, or socket head cap screws.
-
Flange Bolts vs. Hex Bolts: While hex bolts require separate washers to distribute load, flange bolts integrate this feature into the design, saving time and parts.
-
Flange Bolts vs. Carriage Bolts: Carriage bolts are often used in woodworking or applications requiring smooth surfaces. Flange bolts, on the other hand, are tailored for heavy-duty mechanical strength.
-
Flange Bolts vs. Socket Head Cap Screws: Socket head screws are compact and used in precision engineering, but flange bolts excel in scenarios where vibration resistance and load distribution are critical.
Industrial Use Cases of Flange Bolts
-
Automotive Sector – In car engines and transmissions, flange bolts are used extensively because they provide excellent torque distribution and reduce maintenance needs caused by loosening.
-
Pipeline Construction – Oil and gas industries rely on flange bolts to withstand extreme pressures and prevent leakage. The anti-corrosion coatings ensure long service life in harsh environments.
-
Heavy Machinery – Excavators, bulldozers, and cranes require flange bolts for their ability to endure shock, vibration, and heavy loads.
-
Steel Structures – Bridges, towers, and industrial plants benefit from flange bolts’ reliability, as they enhance safety by minimizing the risk of connection failure.
Long-Term Performance Advantage
The integrated design ensures that even under high torque, the fastener maintains stability. This reduces the frequency of inspections and replacements, leading to lower maintenance costs. Additionally, serrated flange bolts, which have teeth-like patterns on the flange, provide an extra locking effect, making them ideal for high-vibration environments such as automotive assembly lines or power plants.
In summary, the practicality of flange bolts comes from their adaptability. They provide industries with a fastening solution that works across multiple applications without compromising safety, strength, or efficiency.
How to Choose the Right Flange Bolt: Key Considerations and FAQs
Selecting the right flange bolt requires evaluating specific criteria based on the application environment. Here are the most important factors:
-
Material Selection: For outdoor or marine applications, stainless steel is recommended due to its corrosion resistance. For heavy machinery, high-grade alloy steel provides the best tensile strength.
-
Coating: If exposed to moisture or chemicals, choose bolts with protective coatings like galvanized or Dacromet finishes.
-
Thread Type: Ensure compatibility with existing nuts or threaded components to avoid assembly issues.
-
Strength Grade: High-tensile bolts (10.9 or 12.9) are ideal for high-load applications, while lower grades may suffice for lighter structures.
-
Head Design: Serrated flange bolts provide additional grip against loosening, making them preferable in vibration-prone environments.
Common Questions About Flange Bolts
Q1: How do flange bolts prevent loosening under vibration?
A1: Flange bolts have an integrated washer-like flange that spreads the clamping force over a wider area. This prevents damage to the joint and reduces the risk of loosening. When serrated flange bolts are used, the teeth on the flange grip the surface, adding extra resistance against vibrations.
Q2: How do I determine the correct size and grade of flange bolt for my project?
A2: The size and grade depend on load requirements, operating conditions, and safety standards. For high-pressure or heavy-duty machinery, grades 10.9 or 12.9 in larger diameters (e.g., M20–M30) are recommended. For lighter assemblies, smaller diameters and standard grades may be sufficient. Consulting engineering guidelines or industry standards ensures the correct choice.
Flange bolts have transformed industrial fastening by providing a combination of strength, efficiency, and safety. Their built-in washer design not only saves time but also enhances performance under demanding conditions. From automotive production lines to massive steel structures, flange bolts consistently deliver reliability and durability.
At QBH, we specialize in manufacturing high-quality flange bolts that meet global standards and exceed industry expectations. Whether your project requires stainless steel for corrosion resistance, high-strength alloy steel for heavy-duty machinery, or customized coatings for unique environments, we provide tailored solutions to match your needs. For further details, product inquiries, or technical support, contact us to discover how QBH can support your next project with precision-engineered fastening solutions.