What is the difference between torsion shear bolts and ordinary steel structure bolts?
In the field of steel structure connection, torsion shear bolts and ordinary high-strength bolts are two mainstream fastening solutions. The differences between the two in structural design, installation process and application scenarios directly affect the connection reliability and construction efficiency, and need to be scientifically selected according to engineering requirements.
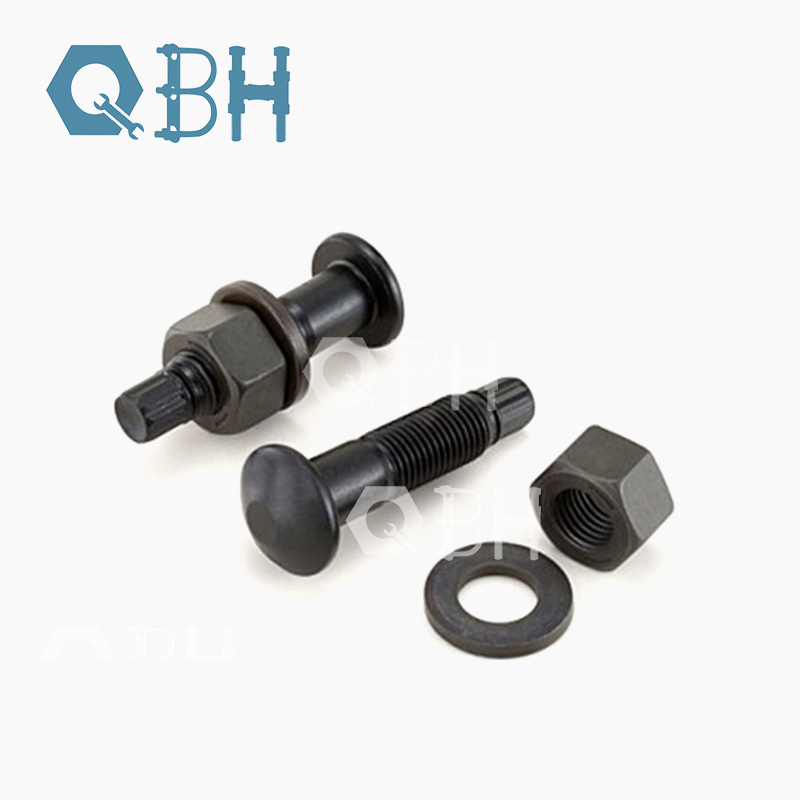

In terms of structural design, the head of the torsion shear bolt has a special plum head, which is connected to the screw through a torque control section. The diameter of this section is smaller than the screw and is a weak point. Ordinary bolts are designed with a hexagonal head, the diameter of the entire rod is consistent, and the preload is generated by tightening the nut. This structural difference makes the preload of the torsion shear bolt less discrete, and the deviation of the same batch can be controlled within ±5%, which is better than the ±15% of ordinary bolts.
The installation method is the most significant difference. The torsion shear bolt uses a special electric wrench to control the preload by cutting off the plum head. When the wrench torque reaches the set value (usually 400-800N・m), the torque control section breaks, and the tightening is completed. No manual judgment is required, and the installation efficiency is 30% higher than that of ordinary bolts. Ordinary bolts need to be tightened in steps by a torque wrench, relying on the workers' experience to control the torque, which can easily lead to insufficient preload or over-tightening due to differences in operation.
In terms of connection performance, the fracture surface of the torsion shear bolt is flat, which can visually inspect the installation quality and avoid the hidden dangers of missing or under-tightening. Its thread is made of high-strength steel of grade 8.8 or above, and with hardened nuts, the anti-slip coefficient is above 0.45, which is suitable for steel structures that bear dynamic loads (such as bridges and cranes). Although the cost of ordinary bolts is 15%-20% lower, its fatigue resistance is weaker and it is more suitable for static load scenarios (such as factory brackets).
Each application scenario has its own focus. Torsion shear bolts are preferred for large steel structure projects (such as stadiums and high-rise buildings). Their standardized installation can reduce human errors and ensure the safety of node connections. Ordinary bolts have more cost advantages in light steel structures and temporary construction. The selection should be based on the load type, construction conditions and quality requirements. The core difference between the two lies in "whether a precise and controllable preload is required", which is also the key reason why the proportion of torsion shear bolts in modern steel structure projects has increased year by year.