What Makes a Carriage Bolt Essential in Fastening?
2025-12-18
This in-depth blog explores the full scope of carriage bolts — what they are, how they differ from other bolts, why they are widely used, how to choose the right one, and where they are applied in real-world projects. With expert hardware knowledge and authoritative references, this article aims to help engineers, builders, and DIYers make smarter fastening decisions. Along the way, we’ll touch on material properties, standards, and key design features. The featured company Jiaxing City Qunbang Hardware Co., Ltd. also offers tailored fastener solutions fitting industrial needs.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Carriage Bolt?
- How Does a Carriage Bolt Work?
- Why Use a Carriage Bolt Instead of Other Fasteners?
- What Sizes and Standards Exist for Carriage Bolts?
- Where Are Carriage Bolts Used?
- How to Choose the Right Carriage Bolt?
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Is a Carriage Bolt?
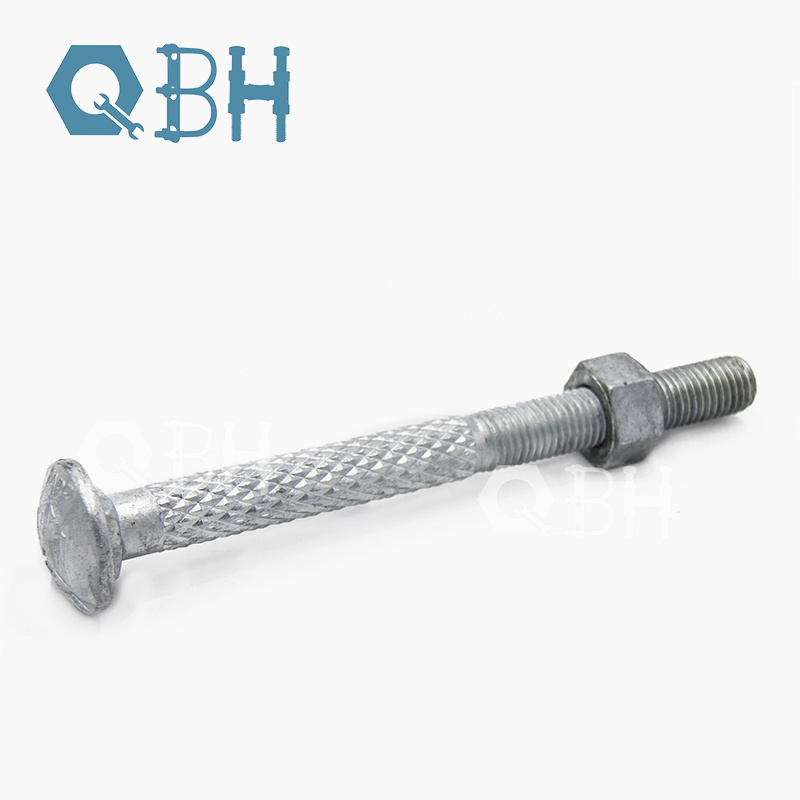
A carriage bolt (also known as a coach bolt or round-head square-neck bolt) is a fastener with a round, domed head and a square section beneath the head that prevents rotation once installed into material. This unique design allows fastening with a nut on one end only, providing smooth, tamper-resistant finishing on the visible side.
- Head Type: Rounded dome (smooth, aesthetic show side)
- Neck: Square or ribbed to prevent rotation
- Shaft: Partial or full thread depending on design
How Does a Carriage Bolt Work?
Carriage bolts work through the square neck embedded in either a pre-cut square hole in metal or by biting into softer materials like wood. Once inserted, the square section prevents the bolt from spinning while the nut on the opposite side is tightened, ensuring a secure firm grip.
This mechanism eliminates the need for holding the bolt head during installation, making carriage bolts particularly advantageous for securing wood-to-metal, wood-to-wood, or metal-to-metal connections.
Why Use a Carriage Bolt Instead of Other Fasteners?
Compared with hex bolts or machine screws, carriage bolts offer the following distinctive advantages:
| Feature | Carriage Bolt | Hex Bolt |
|---|---|---|
| Head Finish | Round & Tamper‑resistant | Hex head exposed |
| Installation | One‑side installation | Requires holding both ends |
| Rotation Prevention | Built‑in (square neck) | Requires tool on head |
| Aesthetics | Smoother surface | Industrial look |
This makes carriage bolts ideal in woodworking, decking, furniture assembly, and anywhere a clean appearance is desired.
What Sizes and Standards Exist for Carriage Bolts?
Carriage bolts are manufactured in both Imperial (fractional inches) and metric sizes, covering a wide range suitable for general construction and industrial use.
- Imperial: Common range from 3/8” to 3/4” diameters (and larger in industrial stock)
- Metric: Standard from M10 to M36 and beyond
- Thread Standards: UNC, UNF, ISO thread profiles
- Materials: Steel, stainless steel, galvanized, alloy, brass
- Specifications: ASME, ISO, BS and various ASTM grades
The variety of sizes and finishes allows selection based on loading requirements, corrosion resistance, and environmental application needs.
Where Are Carriage Bolts Used?
Carriage bolts appear in many applications where a smooth finish and easy installation are priorities:
- Woodworking: Decks, fences, outdoor furniture
- Construction: Posts, railings, and structural joins
- Industrial Machinery: Securing panels and guards
- Agriculture: Farm equipment and fencing hardware
- Marine & Outdoor Equipment: Corrosion-resistant options
These uses take advantage of the carriage bolt’s secure fastening and low‑profile head for safety and aesthetic reasons.
How to Choose the Right Carriage Bolt?
When selecting a carriage bolt, consider the following factors:
- Material & Finish: Stainless or galvanized for outdoor resistance
- Diameter & Length: Sized to thickness of material being fastened
- Thread Type: Full vs partial threads based on application
- Environmental Conditions: Corrosion, vibration, load needs
Correct selection prevents premature failure and ensures proper joint strength and longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the primary purpose of a carriage bolt?
A: The primary purpose of a carriage bolt is to fasten materials together while providing a smooth, round head on one side and a secure, tamper‑resistant fastening on the other. The square neck prevents rotation when tightened.
Q: How does a carriage bolt differ from a hex bolt?
A: Carriage bolts feature a rounded head with a square neck to prevent rotation, whereas hex bolts have an exposed hexagonal head requiring tools to stabilize both ends during fastening.
Q: Can carriage bolts be used outdoors?
A: Yes, carriage bolts with galvanized or stainless finishes are ideal for outdoor applications due to enhanced corrosion resistance.
Q: What materials are carriage bolts made from?
A: Carriage bolts are commonly made from carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steels, sometimes with zinc or hot‑dip galvinized coatings for durability and corrosion resistance.
Q: Do carriage bolts require pre‑drilled holes?
A: In most wood and metal installations, pre‑drilled holes are recommended so that the square neck fits snugly, preventing rotation and allowing proper tightening of the nut.