Why Are Heavy Hex Bolts Essential for Industrial and Structural Applications?
2025-09-09
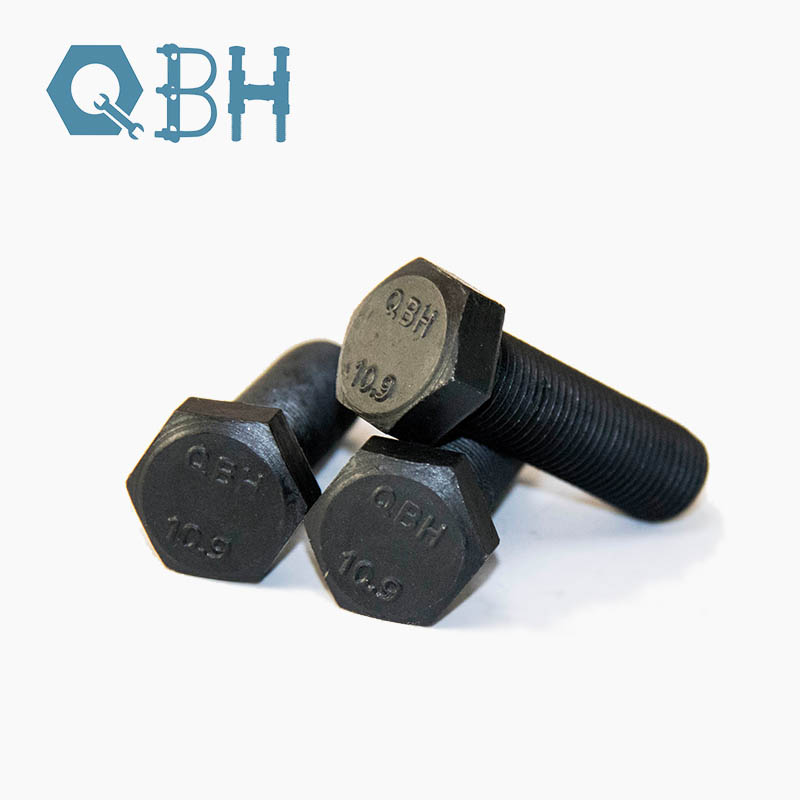
Heavy hex bolts are critical fasteners in a wide range of industrial, construction, and structural applications. Their robust design, combined with precise engineering specifications, ensures that machinery, steel structures, and heavy-duty frameworks remain securely fastened under extreme loads and challenging environmental conditions. Unlike standard hex bolts, heavy hex bolts feature a larger, thicker head and stronger shank, which provides enhanced torque distribution and superior load-bearing capacity. This makes them particularly suitable for projects where safety, reliability, and structural integrity are non-negotiable.
In the engineering and construction industries, the proper selection of fasteners is paramount. Heavy hex bolts are commonly used in bridges, high-rise buildings, steel structures, and heavy machinery assemblies. Their performance directly impacts the safety and longevity of critical infrastructure. In high-stress applications, choosing a substandard bolt can lead to catastrophic failures, costly downtime, and legal liabilities. Therefore, understanding the specifications, materials, and performance characteristics of heavy hex bolts is essential for engineers, procurement specialists, and maintenance teams.
What Makes Heavy Hex Bolts Different from Standard Hex Bolts?
Heavy hex bolts are distinguished from standard hex bolts by their size, strength, and load-handling capabilities. The primary differences include:
| Feature | Standard Hex Bolt | Heavy Hex Bolt |
|---|---|---|
| Head Width | Smaller, conforms to standard hex size | Larger, designed for greater torque distribution |
| Head Thickness | Standard | Extra thick for added strength |
| Shank Diameter | Standard | Typically larger to withstand higher tension |
| Load Capacity | Moderate | High, suitable for structural applications |
| Torque Tolerance | Moderate | High, minimizes risk of bolt failure |
| Material Grades | Often mild steel or low-grade alloys | High-strength steel grades (ASTM A325, A490, ASTM F3125) |
| Surface Treatment | Basic zinc plating or uncoated | Hot-dip galvanized, black oxide, or weather-resistant coatings |
Heavy hex bolts are manufactured according to precise industrial standards, such as ASTM and ISO norms, ensuring consistent quality and performance. The combination of a larger head, thicker shank, and superior material grade makes them indispensable for structural bolting systems. They are particularly effective in pre-tensioned and snug-tight connections, where maintaining a high clamping force is critical.
Key Product Parameters of Heavy Hex Bolts
The following table summarizes typical technical specifications for heavy hex bolts used in industrial applications:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material | Carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel |
| Grade | ASTM A325, A490, F3125, 8.8, 10.9 |
| Diameter Range | 1/2" to 2" (12mm to 50mm) |
| Length Range | 1" to 12" (25mm to 300mm) |
| Thread Type | UNC, UNF, Metric threads |
| Tensile Strength | 120 ksi to 150 ksi depending on grade |
| Surface Finish | Hot-dip galvanized, plain, black oxide, zinc-plated |
| Head Dimensions | Wider and thicker than standard hex bolts |
| Compliance | ASTM, ISO, DIN standards |
| Applications | Structural steel connections, bridges, heavy machinery, industrial frameworks |
These specifications ensure that heavy hex bolts meet the rigorous demands of industrial use, providing reliability, high load-bearing capability, and resistance to environmental factors such as corrosion, vibration, and dynamic loads. Selecting the correct grade, material, and coating is essential to match the operational requirements of the project.
How to Select the Right Heavy Hex Bolt for Your Project?
Choosing the correct heavy hex bolt involves careful consideration of load requirements, environmental conditions, and industry standards. The following steps outline a structured approach:
-
Identify Load Requirements
Calculate the expected tensile and shear forces acting on the bolt. Structural engineers often use load tables and connection design codes to determine the appropriate bolt grade and diameter. -
Select Material and Grade
-
Carbon steel bolts are suitable for general industrial use.
-
Alloy steel bolts, such as ASTM A490, offer higher tensile strength for critical structural applications.
-
Stainless steel bolts provide excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for outdoor or marine environments.
-
-
Determine Bolt Dimensions
Length and diameter should be selected based on the thickness of connected components and the required embedment. Proper thread engagement is crucial for maximum load transfer. -
Choose Surface Finish
Surface coatings like hot-dip galvanization improve corrosion resistance, especially in outdoor or chemically aggressive environments. Plain or black oxide finishes are suitable for indoor use where corrosion risk is minimal. -
Verify Compliance with Standards
Ensure that the selected bolts meet relevant standards, such as ASTM A325, A490, or ISO 898-1. Certified bolts guarantee consistent mechanical properties and reliability in critical applications. -
Installation Considerations
Correct torque application is critical. Over-tightening or under-tightening can compromise the structural integrity of the connection. Using calibrated torque wrenches and following manufacturer guidelines ensures optimum performance.
By following this systematic approach, engineers and project managers can ensure that their heavy hex bolts provide maximum strength, durability, and safety for any industrial or structural application.
Frequently Asked Questions About Heavy Hex Bolts
Q1: Can heavy hex bolts be reused after removal?
A1: Heavy hex bolts may sometimes be reused, but it depends on their material grade, load history, and thread condition. High-strength bolts, especially those used in structural steel connections, are often designed for single-use under pre-tensioned conditions. Reusing such bolts can compromise joint integrity, so it is recommended to inspect them thoroughly for thread wear, deformation, or surface damage before considering reuse. When in doubt, replace them with new bolts that meet the original specifications.
Q2: What is the difference between ASTM A325 and A490 heavy hex bolts?
A2: ASTM A325 bolts are made from medium carbon steel with a minimum tensile strength of 120 ksi and are suitable for general structural applications. ASTM A490 bolts, however, are high-strength alloy steel bolts with a minimum tensile strength of 150 ksi, designed for critical structural connections requiring higher load-bearing capacity. Additionally, A490 bolts typically require heat treatment to achieve the specified mechanical properties and may have stricter installation torque requirements compared to A325 bolts.
Heavy hex bolts are indispensable components for ensuring the structural integrity and safety of industrial and construction projects. Their superior design, material strength, and compliance with international standards make them the go-to choice for engineers and builders seeking reliable performance in demanding environments. Whether it is a bridge, high-rise building, or heavy machinery assembly, selecting the appropriate heavy hex bolt ensures that critical connections remain secure over the long term.
For top-quality heavy hex bolts that meet international standards and are backed by professional expertise, QBH offers a comprehensive range designed for strength, reliability, and durability. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and receive personalized solutions tailored to your industrial or structural applications.